Summary
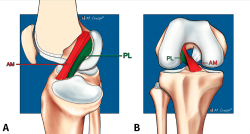
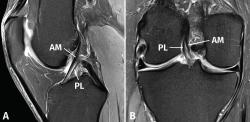
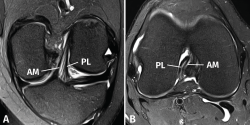
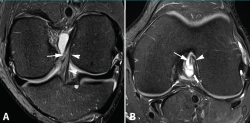
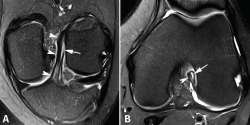
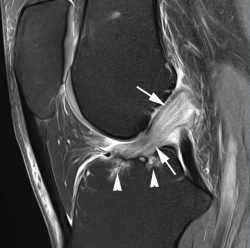
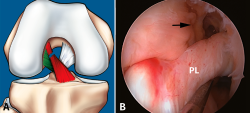
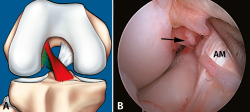
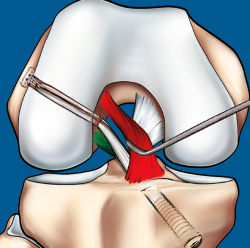
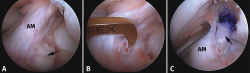
Las lesiones parciales del ligamento cruzado anterior (LCA) siguen representando un dilema diagnóstico y terapéutico para el cirujano ortopédico. Aunque son lesiones poco frecuentes, pueden ser sintomáticas y condicionar un trastorno funcional significativo. A la hora de realizar un diagnóstico correcto, además de la historia clínica y los estudios de imagen, la exploración física mediante la maniobra del pivot shift, tanto en la consulta como bajo anestesia, es clave a la hora de valorar la inestabilidad funcional del LCA y el tratamiento más adecuado. En la actualidad, las técnicas quirúrgicas anatómicas individualizadas permiten la reconstrucción artroscópica del fascículo lesionado. Estas técnicas preservan las fibras intactas con el objetivo de restaurar la anatomía del LCA y muestran buenos resultados funcionales. Recientemente, se han desarrollado técnicas de reparación y aumentación del fascículo lesionado en un intento de lograr una cicatrización estable del mismo. El propósito de esta revisión es clarificar el manejo clínico y la estrategia de tratamiento en las roturas parciales del LCA.
Abstract
Partial injuries of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) continue to represent a diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma for the orthopedic surgeon. Although they are uncommon injuries, they could be symptomatic and condition a significant functional impairment. To make a correct diagnosis of partial ACL injuries, in addition to the clinical history and imaging studies, the physical examination mainly by means of the pivot shift maneuver, both in the office and under anesthesia, is key in assessing functional instability of the ACL and to select the most appropriate treatment. Currently, individualized anatomical surgical techniques allow arthroscopic reconstruction of the injured fascicle. These techniques preserve the intact fibers and restore the anatomy of the ACL with good functional results. Recently, techniques of repair and augmentation of the injured fascicle have been developed in an attempt to achieve stable healing of it. The purpose of this review is to clarify the clinical management and treatment strategy in partial ACL tears.
Article
Figures and tables
References
Downloads
Licence
Este contenido es de acceso abierto (Open-Access) y se ha distribuido bajo los términos de la licencia Creative Commons CC BY-NC-ND (Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional) que permite usar, distribuir y reproducir en cualquier medio siempre que se citen a los autores y no se utilice para fines comerciales ni para hacer obras derivadas.