Resumen
Las fracturas de húmero distal tienen una incidencia de un 2%. En jóvenes se producen por accidentes de alta energía, mientras que en ancianos con hueso osteoporótico, se suelen producir por accidentes de baja energía.
El objetivo de este trabajo es hacer una revisión de los aspectos más importantes del manejo de este tipo de fracturas y sus generalidades.
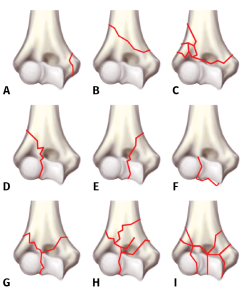
Para su diagnóstico es fundamental la exploración física, que consistirá en constatar la deformidad y la impotencia funcional, haciendo especial hincapié en el estado de las partes blandas, ya que estas pueden condicionar o demorar el tratamiento definitivo, y también descartar lesiones neurovasculares. El estudio radiológico comenzará por unas radiografías simples del codo (anteroposterior y lateral) y en la mayoría de estas fracturas, especialmente si son complejas y con afectación articular, se recomienda la realización de una tomografía axial computarizada para completar el estudio. El tratamiento de estas fracturas es principalmente quirúrgico en la gran mayoría de los casos. Su objetivo es restaurar la anatomía previa, aportar una fijación estable y comenzar la movilidad a la mayor brevedad posible. El tratamiento conservador se reserva para pacientes con contraindicaciones absolutas para la cirugía o para la anestesia.
Como conclusión, son fracturas complejas, técnicamente demandantes que con frecuencia asocian complicaciones y/o secuelas.
Abstract
Distal humerus fractures have an incidence of 2%. In young people they are caused by high energy accidents; while in the elderly with osteoporotic bone, they are usually caused by low-energy accidents.
The objective of this work is to review the most important aspects of the management of this type of fractures. Summarizing the anatomical aspects that must be taken into account above all for the subsequent treatment, the physical and radiological examination, and the different treatment options and their indications.
The exploration of these fractures will consist of verifying the deformity and functional impotence, with special emphasis on the state of the soft tissues which can condition or delay the definitive treatment and rule out neurovascular injuries.
The radiological study begins with simple x-rays of the elbow (anteroposterior and lateral) and in most of these fractures, especially in complex ones with joint involvement, a computed tomography scan is recommended to complete the study.
The treatment of these fractures is mainly surgical in the vast majority of cases. Its objective is to restore the previous anatomy, provide a stable fixation and begin mobility as soon as possible. Conservative treatment is reserved for patients with absolute contraindications to surgery or anesthesia.
In conclusion, they are complex, technically demanding fractures that frequently associate complications and/or sequelae.
Artículo
Figuras y tablas
Referencias
Descargas
Licencia
Este contenido es de acceso abierto (Open-Access) y se ha distribuido bajo los términos de la licencia Creative Commons CC BY-NC-ND (Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional) que permite usar, distribuir y reproducir en cualquier medio siempre que se citen a los autores y no se utilice para fines comerciales ni para hacer obras derivadas.